Introduction
To make the target market aware of the new product it is important to heavily promote it. A special introductory price may help push the product. The product is new to the mark and it takes some time after introduction for the product to become popular.
Growth
As sales and profitability increase, the selling price may be reduced to make the product more attractive. Continued advertising around the brand name will help to sustain sales. The marketing team may consider expanding its distribution, to reach more consumers. Interest grows, it is new and popular and many units are sold, these sales grow until they reach a peak.
Maturity
The product has reached a stage were no new interest can be generated. The sales level of and profit is consistent as their is still a demand for the product.
Decline
The product has lost it's novelty, fashion or it's seasonal appeal (common with products like Christmas cards) and sales began to drop as the demand for the product lessons. Sales decrease until the sales are negligible. At this point the product usually is changed or goes out of production.
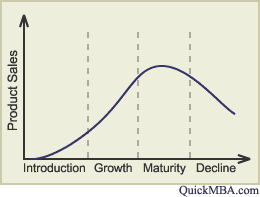 |
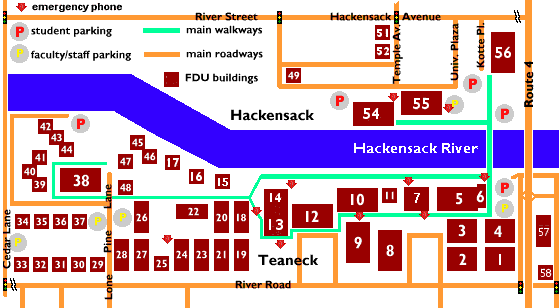
| Product Lifecycle is most commonly expressed graphically |